Installation¶
Note
Please see the Overview for the server-level requirements before attempting to use LSCache.
Server-Level¶
Configure the Server¶
LSCache must be set up at the server level before it can be made available to any sites on the server.
Tip
If you are a site owner and you don't have access to your server's admin functions, chances are your hosting provider has already done this setup for you, or can help you to complete it.
See Configure Cache Root and Cache Policy for instructions.
Basic Rewrite Rules¶
Once the server level configuration is complete, it's time to set up the rewrite rules that govern the LSCache engine.
Add these lines to the virtual host's document root .htaccess file:
<IfModule litespeed>
CacheLookup on
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !/admin/ [NC]
RewriteRule .* - [E=cache-control:max-age=120]
</IfModule>
And with that, you have just enabled caching on your site. All pages that are not in the admin subdirectory, will be cached publicly for two minutes.
This is a very basic set of rules. You can change the RewriteCond directive to include or exclude whatever pages you like. You can adjust cache-control to use private cache instead of public, or cache pages for a week (though, we don't recommend that for caching without a plugin). See Configuration for a host of more powerful examples, including some suggested settings for well-known web apps.
Verify Your Site is Being Cached¶
Video
See a video demonstration of this topic here.
LSCache Check Tool¶
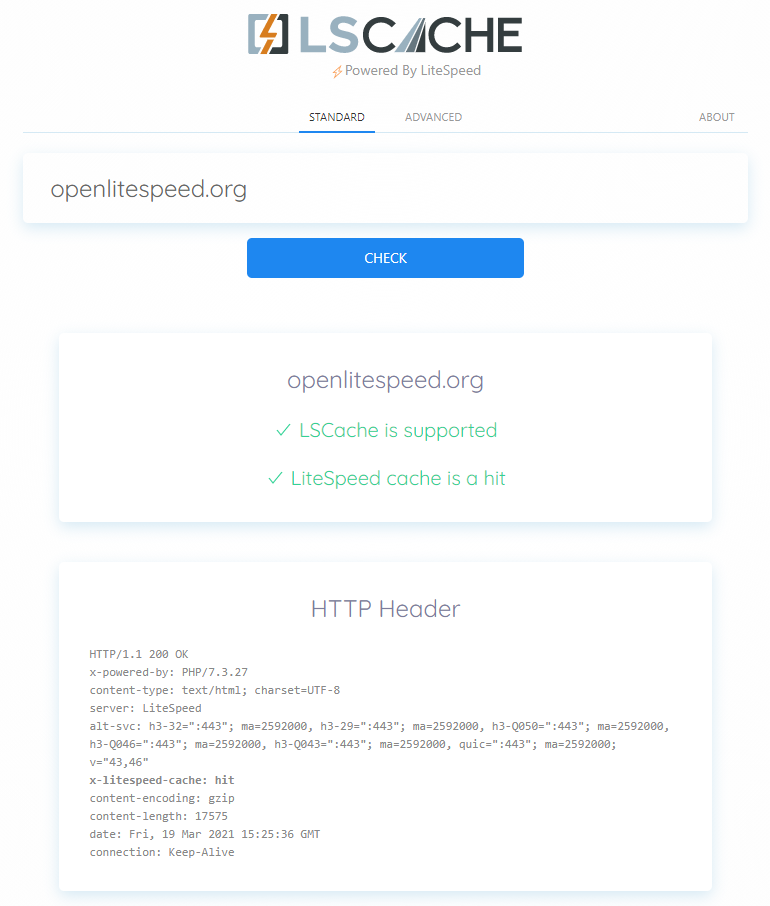
There's a simple way to see if a URL is cached by LiteSpeed: the LSCache Check Tool.
Enter the URL you wish to check, and the tool will respond with an easy-to-read Yes or No result, and a display of the URL's response headers, in case you want to examine the results more closely.
In addition to LSCache support, the tool can detect cache hits, and can detect when sites are using LiteSpeed Web ADC or QUIC.cloud CDN for caching.
Additionally, a Stale Cache Warning will alert you if browser cache is detected on dynamic pages. This is because browser cache may interfere with the delivery of fresh content.
Manual Lookup¶
You can verify a page is being served from LSCache through the following steps:
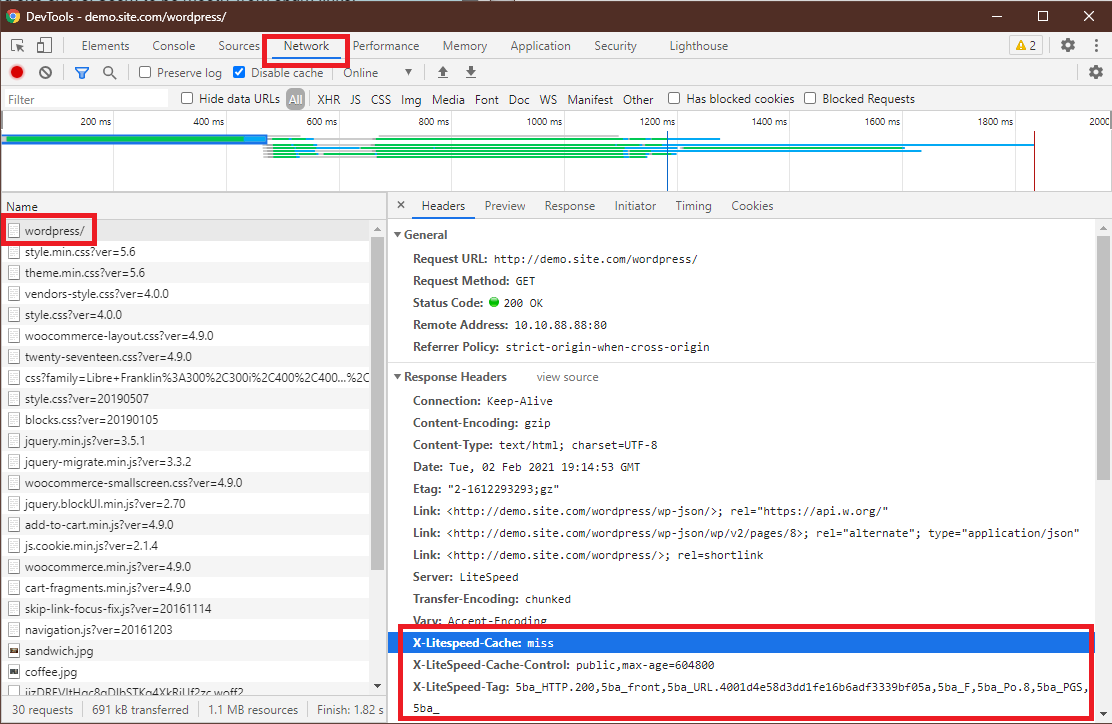
- From a non-logged-in browser, navigate to your site, and open the developer tools (usually, right-click > Inspect). Open the Network tab.
- Refresh the page.
- Click the first resource. This should be an HTML file. For example, if your page is
http://example.com/webapp/, your first resource should either be something likeexample.com/webapp/orwebapp/. -
You should see headings similar to these:
These headings mean the page had not yet been cached, but that LiteSpeed has now stored it, and it will be served from cache with the next request.X-LiteSpeed-Cache: miss X-LiteSpeed-Cache-Control:public,max-age=1800 X-LiteSpeed-Tag:B1_F,B1_ -
Reload the page and you should see
X-LiteSpeed-Cache: hitin the response header. This means the page is being served by LSCache and is configured correctly.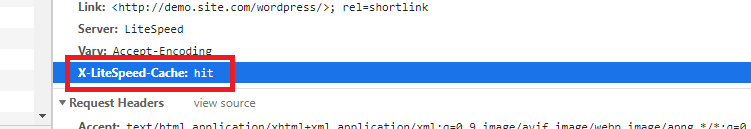
Alternative Headers
The X-LiteSpeed-Cache header is most common, but you may see X-LSADC-Cache if your site is served by LiteSpeed Web ADC.
You may also see X-QC-Cache and X-QC-Pop if your site is served via QUIC.cloud CDN. The former indicates the cache status (hit or miss) and the latter indicates what PoP location (such as NA-US-LGA-33) served this response.
These alternative headers are also an indication that LSCache is working properly on your site.
Important
If you don't see X-LiteSpeed-Cache: hit or X-LiteSpeed-Cache: miss (or any of the alternative headers), then there is a problem with the LSCache configuration.
Non-Cacheable Pages¶
Sometimes there are pages which should not be cached. To verify that such pages have indeed been excluded from caching, check the developer tools as described above.
You should see headings similar to these:
X-LiteSpeed-Cache-Control:no-cache, esi=on
X-LiteSpeed-Tag:B1_F,B1_
X-LiteSpeed-Cache-Control, when set to no-cache, indicates that LiteSpeed Server has served your page dynamically, and that it was intentionally not served from cache.